Size:43x20x16cm
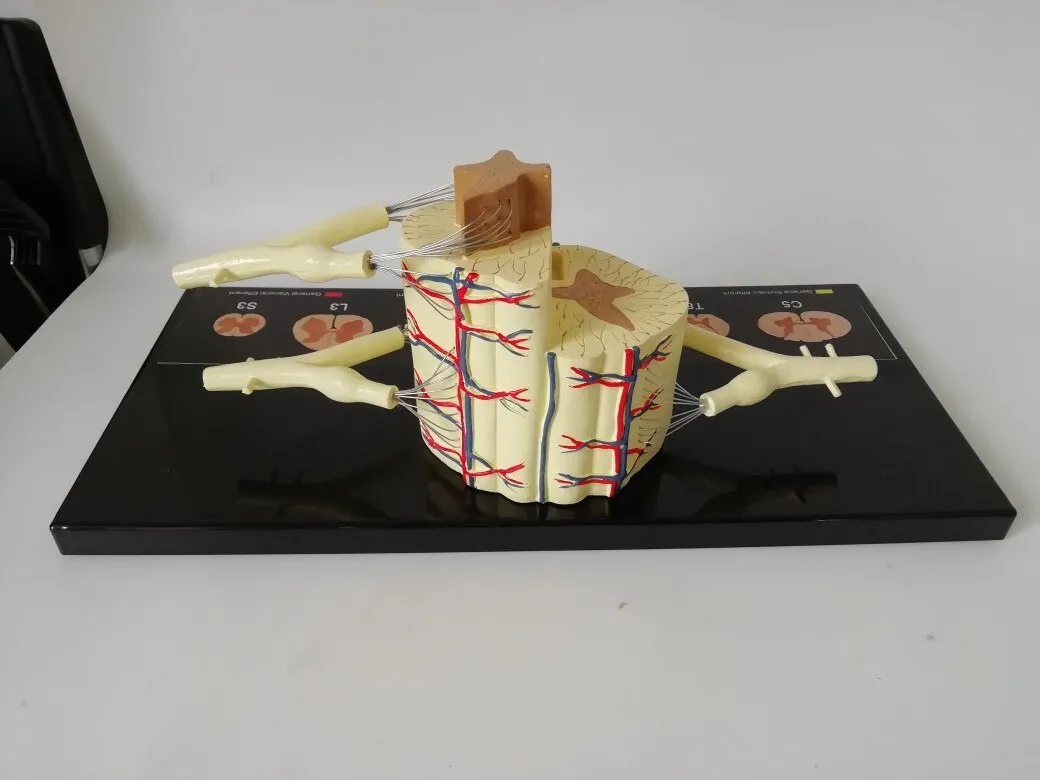
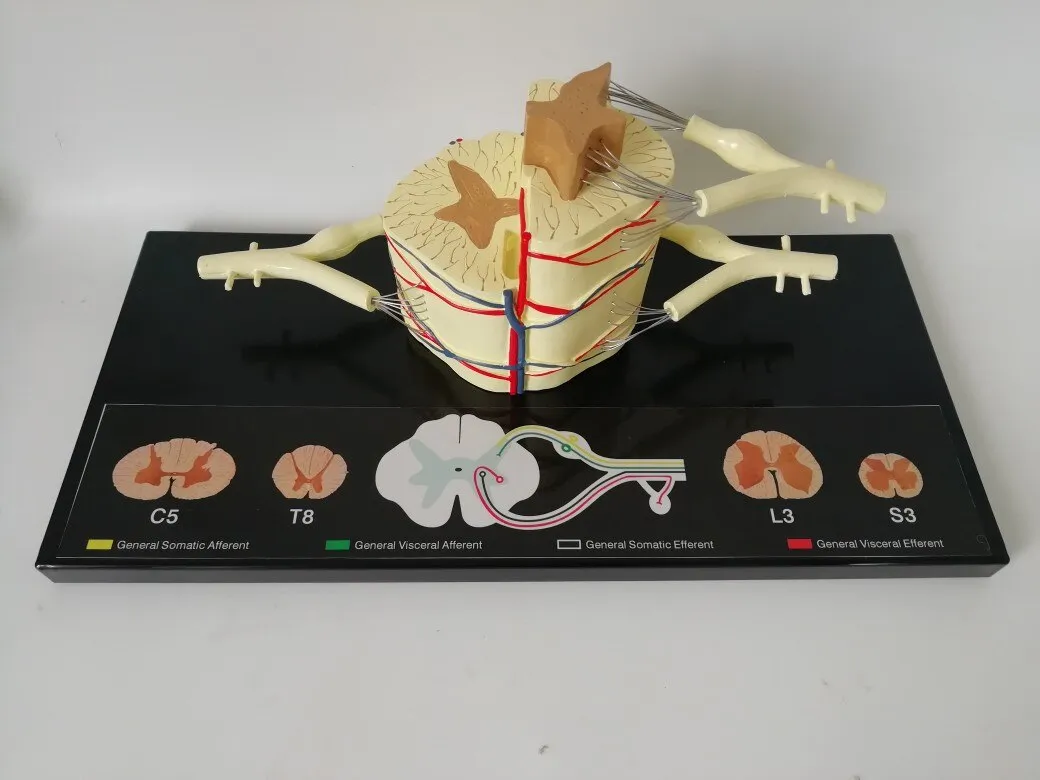
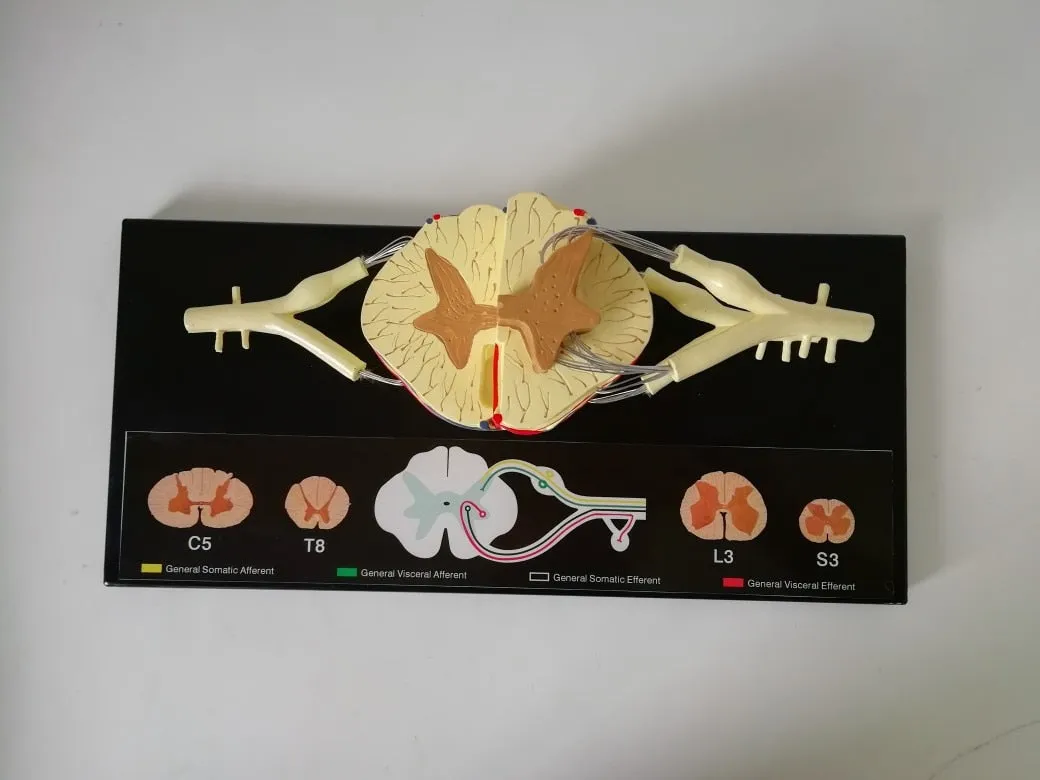
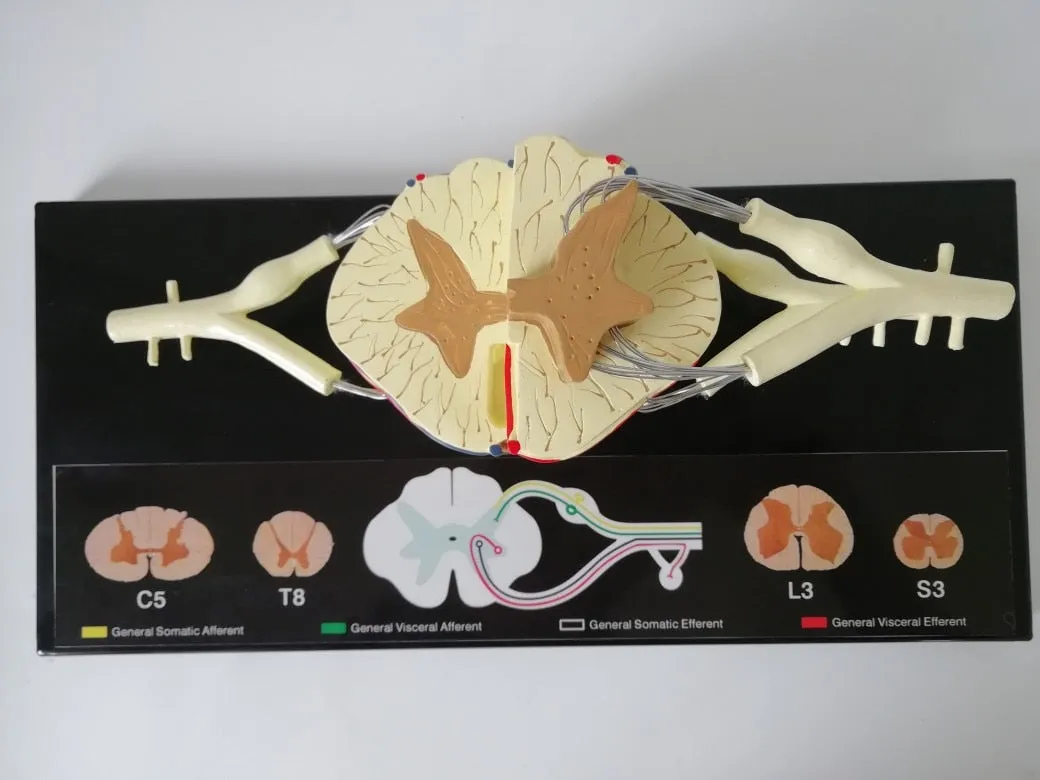
Spinal nerves are magnified 5 times, made of high-quality PVC material,
A total of 31 pairs of spinal nerves, connected to the spinal cord, are distributed in the muscles of the trunk, ventral side and limbs, and are responsible for the sensation and movement below the neck.
Morphology of spinal nerves
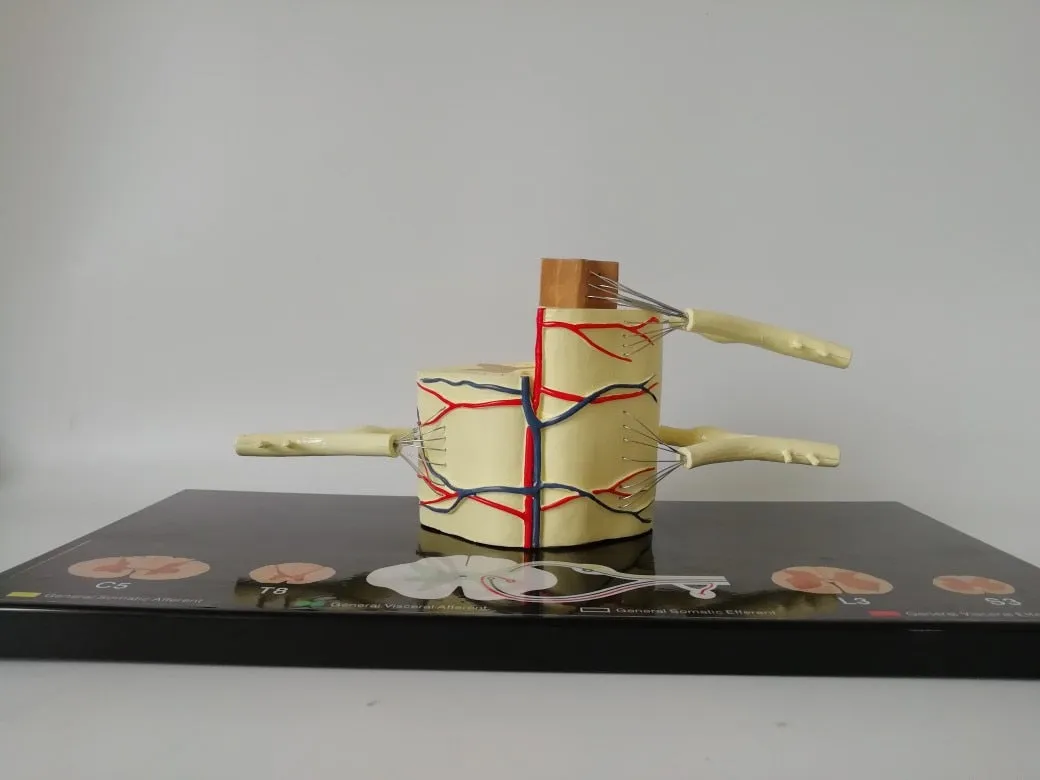
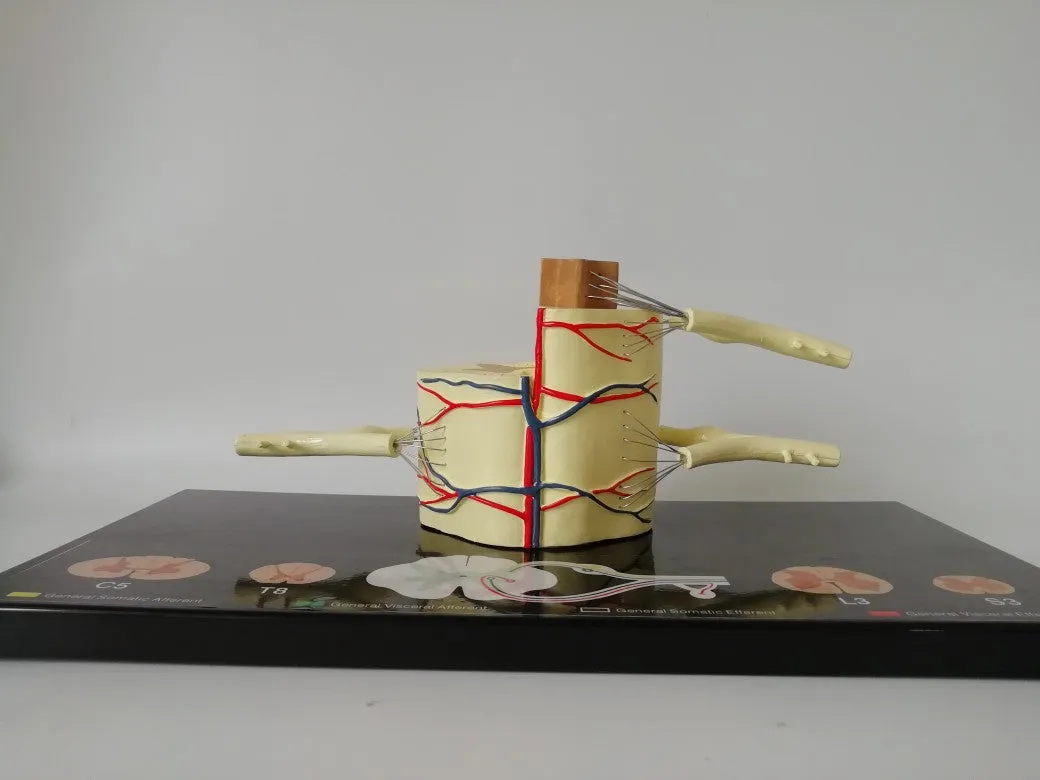
Each pair of spinal nerves is connected to the spinal cord by the ventral root and the dorsal root. The anterior and posterior roots are composed of root filaments composed of many nerve fiber bundles. The anterior root is motility, the posterior root is sensory, and the posterior root is slightly thicker than the anterior root. The two synthesize a spinal nerve trunk at the intervertebral foramen. Mixed with sports fibers in the dry.
The posterior root has an oval enlargement near the intervertebral foramen, which is called sumal ganglia. The 31 pairs of spinal nerves include 8 pairs of cervical nerves, 12 pairs of thoracic nerves, 5 pairs of lumbar nerves, 5 pairs of sacral nerves, and a pair of coccygeal nerves. The first cervical nerve trunk passes through the spinal canal between the atlas and the occiput, the second to seventh cervical nerve trunks pass through the spinal canal through the intervertebral foramen above the cervical vertebra in the same order, and the eighth cervical nerve trunk passes through the vertebrae below the seventh cervical vertebra. The interforamen pass through, 12 pairs of thoracic nerve trunks and 5 pairs of lumbar nerve trunks pass through the intervertebral foramen under the same ordinal number of vertebrae. The first to fourth sacral nerves pass through the same ordinal number of anterior and posterior sacral foramen, and the fifth sacral nerve passes through the same ordinal number of anterior and posterior foramen. The nerve and coccyx nerve pass through the sacral hiatus. Because the spinal cord is short and the spinal canal is long, the directions and lengths of the spinal nerve roots in each segment of the spinal canal are different. The cervical nerve roots are short, the stroke is nearly horizontal, the chest is obliquely downward, and the lumbosacral nerve roots are longer. It descends almost vertically in the spinal canal and forms cauda equina. In the intervertebral foramina, the spinal nerves have an important adjacent relationship. The front is the intervertebral disc and the vertebral body, and the back is the intervertebral joint and the ligamentum flavum. Therefore, spinal diseases, such as herniated discs and vertebral fractures, often involve spinal nerves, causing sensory and movement disorders.

 Cart(
Cart(